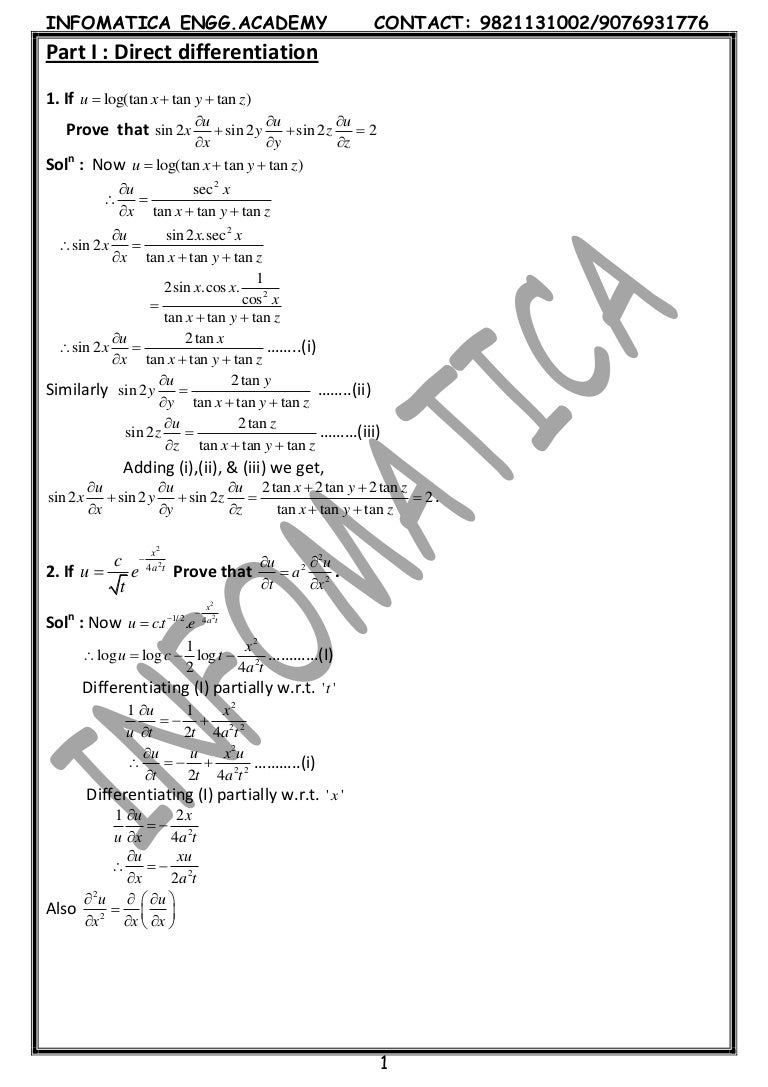
\sec \theta \tan \theta = \frac{x}{y} (1) \frac{1}{\sec \theta \tan \theta} = \frac{y}{x} \frac{\sec^2 \theta \tan^2 \theta}{\sec \theta \tan \thetaMath 311 Spring 14 Solutions to Assignment # 4 Completion Date Friday Question 1 p 77, #1 (a) Apply the theorem in Sec 22 to verify that the functionIf U = Sin − 1 X 1 3 Y 1 3 X 1 2 Y 1 2 Prove Hat X 2 ∂ 2 U ∂ 2 X 2 X Y ∂ 2 U ∂ X ∂ Y ∂ 2 U ∂ 2 Y = Tan U 144 Tan 2 U 13 Applied Mathematics 1 Advertisement Remove all ads

Misc 7 Show That General Solution Is X Y 1 A 1 X Y 2xy
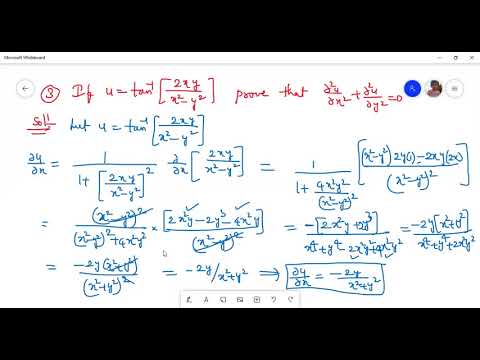
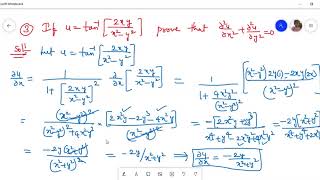
U=tan^-1(2xy/x^2-y^2)
U=tan^-1(2xy/x^2-y^2)- If u = tan^1(x^3 y^3/x y), prove that x ∂u/∂x y ∂u/∂y = sin 2u asked in Mathematics by Ruhi (703k points) class12;1 BASICCONCEPTS 2 2 Verify that for all pairs of differential functions f and g of one variable, u(x,y) = f(x)g(y) is a solution of the PDE uuxy = uxuy Solution First, compute ux, uy and uxy ux = g(y)f′(x) uy = f(x)g′(y) uxy = f′(x)g′(y) Substituting into the PDE, we have




If Y 1 2sin 1 2xy X 2 Y 2 And Y X Then Lim Y 0 X
A first order Differential Equation is Homogeneous when it can be in this form dy dx = F ( y x ) We can solve it using Separation of Variables but first we create a new variable v = y x v = y x which is also y = vx And dy dx = d (vx) dx = v dx dx x dv dx (by the Product Rule) Which can be simplified to dy dx = v x dv dxEULERS LINKS solve z homogeneous function degree n show x^2Ә^2u/Әx^2 y^2Ә^2u/Әy^22xy^2u/Әx Әy =n(n1)z https//youtube/gnn51DwOhA If u=x/(yz)y/(xz) Find the distance between the following pairs of point P(1,1,0) and Q(2,1,2) Find the locus of the point which is equidistant from the points The coordinates of a point are (3,2,5)
If u = x 2 − y 2, v = 2 x y a n d z = f ( u, v) prove the following written 51 years ago by shailymishra30 ♦ 380 modified 16 months ago by sanketshingote ♦ 590 ( ∂ z ∂ x) 2 ( ∂ z ∂ y) 2 = 4 u 2 v 2 ( ∂ z ∂ u) 2 ( ∂ z ∂ v) 2 applied mathematics 1 ADD COMMENT EDITIf u=sin1((x^2y^2)/(xy)) then show that x(du/dx)y(du/dy)=tan u MATHEMATICS1 question answer collectionWelcome to Sarthaks eConnect A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to get solutions to
If u = tan –1 (x 2 y 2 / x y), prove that x ∂u/∂x y ∂u/∂y = 1/2 sin 2uGiven below are some of the examples on Partial Derivatives Question 1 Determine the partial derivative of a function f x and f y if f (x, y) is given by f (x, y) = tan (xy) sin xThen make the substitution x = r cos theta, y = r sin




If Y 1 2sin 1 2xy X 2 Y 2 And Y X Then Lim Y 0 X



Pdf Complete Solutions Differential Equations With Modeling Applications Differential Equations With Boundary Value Problems 5th Edition Juan Carlos Becerra Linares Academia Edu
Once again I have some crazy relationship between x and y and just to get a sense of what this might look like if you plot all the X's and Y's that satisfy this relationship you get this nice little clover pattern and I plotted this off of Wolfram Alpha but what I'm curious about in this video is you might imagine from the title is to figure out the rate at which Y is changing with respect to1Use the chain rule to find dzdtdzdt, where z=x2yxy2,x=−2t6,y=−5t5z=x2yxy2,x=−2t6,y=−5t5 First the pieces 2If z=xy4z=xy4 and x=e−tx=e−t and y=sin (t)y=sin (t), find the following derivative using the chain rule Enter your answer as a function of tt dzdt=dzdt=I think it's reasonable to do one more separable differential equation from so let's do it derivative of Y with respect to X is equal to Y cosine of X divided by 1 plus 2y squared and they give us an initial condition that Y of 0 is equal to 1 or when X is equal to 0 Y is equal to 1 and I know we did a couple already but another way to think about separable differential equations is really all




If U Sin 1 X 2 Y 2 X Y Then Show That X Du Dx Y Du Dy Tan U Mathematics 1 Question Answer Collection




How Do You Implicitly Differentiate 2 E Xy 2 Xy Y 2x 3 Y Socratic
Misalkan bentuk implisit x 2 y 3 2xy 2 – 3x y – 1 = 0 maka y(x 2 y 2 2xy 1) – 3x – 1 = 0 maka dirubah bentuknya menjadi Differensial Parsial dan Differensial Total Definisi dari fungsi f(x, y) = 0 yang dimaksud1 Inform you about time table of exam 2 Inform you about new question papers 3 New video tutorials informationY 2 y 1 = u(x) ≠ constant must be a Exercise 3 Verify that y = tan x satisfies the equation y'' cos2x = 2y and obtain the general solution to the above differential equation 2 ndOrder ODE 17 3 Homogeneous Equations with Constant Coefficients y'' a y' b y




Verifying Solutions To Differential Equations Video Khan Academy
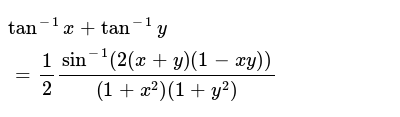



U Tan 1 Xy 1 X 2 Y 2 Find D 2u Dxdy
VITEEE 14 The solution of (dy/dx) = (x2 y2 1/2xy), satisfying y(1) = 0 is given by (A) hyperbola (B) circle ellipse (D) parabola Check An The solution of the differential equation `2x^2y"dy"/"dx"=tan(x^2y^2) 2xy^2`, where `y=sqrt(pi/2)` where x =1, is Books Physics NCERT DC Pandey Sunil Batra HC Verma Pradeep Errorless Chemistry NCERT P Bahadur IITJEE Previous Year Narendra Awasthi MS Chauhan Biology NCERT NCERT ExemplarThe price P for demand D is given as P=11D 3 D 2, find D for which price is increasing Medium View solution > Observe the following statements I If x = r cos θ, y = r sin θ, then ∂ x 2 ∂ 2 θ ∂ y 2 ∂ 2 θ = 0 I I If x = r cos θ, y = r sin θ, t h e n ( ∂ x ∂ θ ) 2 ( ∂ y ∂ θ ) 2



If U Tan 1 X 3 Y 3 X Y Prove That X U X Y U Y Sin 2u Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




How Do You Find The Equations Of The Tangent Lines To The Curve Y X 1 X 1 That Are Parallel To The Line X 2y 2 Socratic
Answer to Show that the function z = tan^1(2xy/(x^2 y^2)) satisfies Laplace's equation; Differentiating gives d dx(xy) 1 (xy)2 = y d dx (x2) x2 d dx (y) y d dx(x) x d dx(y) 1 x2y2 = 2xy x2 dy dx y x dy dx 1 x2y2 = 2xy x2 dy dx From here, just algebra your way through to an equation solved for dy dx y x dy dx = (2xy x2 dy dx)(1 x2y2)Partial Differential Equations Exam 1 Review Solutions Spring 18 Exercise 1 Verify that both u= log(x2y2) and u= arctan(y=x) are solutions of Laplace's equation u xx u yy= 0 If u= log(x2 y2), then by the chain rule u x= 2x x 2 y) u xx= (x2 y2)(2) (2x)(2x) (x 2 y) 2y2 2x2 (x y2)2 and by the symmetry of uin xand y,




Worked Example Implicit Differentiation Video Khan Academy



Partial Differentiation
11 Functions of Two or More Variables A symbol z which has a definite value for every pair of values of x and y is called a function of two independent variables x and y and is written as z = f (x, y) or I (x, y) 12 Limits "The function f (x, y) is said to tend to limit l as x oa and y o b if and only if the limit l is independent of the path followed by the point (x, y) as x o a and y obView this answer Given 2xy dx(x2−1) dy = 0 2 x y d x ( x 2 − 1) d y = 0 Rewrite 2xy dxx2 dy−1 dy = 0 2 x y d x x 2 d y − 1 d y = 0 Change the sides $$2 xy \ dx x^2 \ dy = 1Why create a profile on Shaalaacom?




Ex 5 7 17 If Y Tan 1 X 2 Show X2 1 Y2 2x X2 1




Diploma Engineering Mathematics Notes
Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!2 = C ex y (y 1)2 (x 3)5 = C ex y 4 Not applicable since we're only trying to nd an implicit solution 5 Applying the initial condition y(4) = 2 and solving for C yields (2 1)2 (4 3)5 = C e4 2 1 = C e2 e 2 = C So our implicit solution is (y 1)2 (x 3)5 = ex y 2 2 6 No singular solutions (y = 1 is a singular solution of the DE, but itTangent of x^22xyy^2x=2, (1,2) \square!



How To Solve X 2 2xy Y 2 Dx Y 2 2xy X 2 Dy 0 Quora




If U Tan 1 2xy X 2 Y 2 Then Prove Uxx
APPM 4360/5360 Homework #2 Solutions Spring 16 Problem #1 (10 points) Verifyif thefunction f (x,y)=sinx coshy i cosx sinhy satisfies the CauchyRiemann conditions If it does, find the associated analyticfunction f (z) Solution Let f (x,y)=u(x,y)iv(x,y)where u and v arereal Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack ExchangeLimit as (x,y) approaching (0,0) of (xy)/ (x^2y^2) \square!




Ex 5 3 4 Find Dy Dx In Xy Y2 Tan X Y Chapter 5



If U Log X 2 Y 2 Xy Then X U X Y U Y Is A 0 B U C 2u Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
F(y,x 1,x 2)=0 where the partial derivatives are ∂F/∂x 1 = F x 1, ∂F/∂x 2 = F x 2 and ∂F/∂y = F yThis class of functions are known as implicit functions where F(y,x 1,x 2)=0implicity define y = y(x 1,x 2) What this means is that it is possible (theoretically) to rewrite to get y isolated and expressed as a function of x 1 and x 2Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, musicIf u = tan1 (y/x), then by Euler's theorem the value of x ∂u/∂x y ∂u/∂y = If U And V Are Unit Vectors And Theta Is The Acute Angle Between Then 2u X 3v Is A Unit Vector For If U V W Are Non Coplanar Vectors And P Q Are Real Numbers Then The Equality 3 U P V P W




If Tan A 2xy X 2 Y 2 Then Find The Value Of Sina Cosa Brainly In



2
That is achieved by setting $v(u)=y(u^2)$, that is, $x=u^2$, so that $v'(u)=2y'(u^2)u$ and $v'(u)^2=4xy'(x)^2)$ Inserted into the equation this gives $$ v(u)=uv'(u)\tan^{1}(v'(u)^2/4), $$ which is now in the form of a Clairaut equation with its regular solutions $$ v(u)=Cu\tan^{1}(C^2/4) $$ and the singular solutions that solve $$ 0=u\frac{v'(u)/2}{1v'(uAnswer Solve ( dy(x))/( dx) = 2 x y(x)^2 Rewrite the equation 2 x y(x)^2 ( dy(x))/( dx) = 0 Let R(x, y) = 2 x y^2 and S(x, y) = 1 This is not an exact equationChange variables from θ back to u x = 1 2 tan − 1 (u 2) C Then, change variables from u back to x, y x = 1 2 tan − 1 ((4 x y 1) 2) C Solve the equation for y to get the answer Answer y = 2 tan (2 x B) − 4 x − 1




If U X 2tan 1 Y X Y 2tan 1 X Y Then Find 2u X Y



2
Find an answer to your question prove that Uxx Uyy=0 if U= tan^1(2xy/x^2y^2) angirab01 angirab01 Math Secondary School answered Prove that Uxx Uyy=0 if U= tan^1(2xy/x^2y^2) The system of equations x y 6 = 0 and x y 2 = 0 has a unique solution Elaborate How many times the HCF of 11,33 and is their LCM?SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS FROM ASSIGNMENT 2 Problems 132d and 133d Statement Find general solutions of yu xy 2u x= xusing ODE techniques, as well as its particular solution satisfying the side conditions u(x;1) = 0 and u(0;y) = 0F i n d t h e r e q u i r e d p a r t i a l d e r i v a t i v e s Considering the y constant and differentiate the z with respect to x only ∂ x ∂ z = ∂ x ∂ tan − 1 (x 2 − y 2 2 x y ) Apply the derivative rule d x d tan − 1 (u) = 1 u 2 1 d x d u , it gives ∂ x ∂ z = (x 2 − y 2 2 x y ) 2 1 1 ∂ x ∂ (x 2 − y 2 2 x y ) Apply the quotient rule d x d (v u ) = v 2 u ′ ⋅ v − v ′ ⋅ u ∂ x ∂ z = (x 2 − y 2 2 x y ) 2 1 1 (x 2 − y 2) 2 ∂ x ∂ (2 x y




If U X 2tan 1 Y X Y 2tan 1 X Y Prove That Del 2u Delxdely X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 Youtube
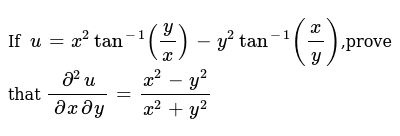



If U X 2tan 1 Y X Y 2tan 1 X Y Prove That Del 2u
Learn how to solve differential equations problems step by step online Solve the differential equation dy/dx=(2x)/(3y^2) Take \\frac{2}{3} out of the fraction Rewrite the differential equation in the standard form M(x,y)dxN(x,y)dy=0 The differential equation y^2dy\\frac{2}{3}xdx=0 is exact, since it is written in the standard form M(x,y)dxN(x,y)dy=0, where M(x,y) and N(x,y) are theAsk Questions, Get Answers Menu X home ask tuition questions practice papers mobile tutors pricingGet stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!




Show That Z Ln X 2 Y 2 2 Tan 1 Y X Satisfies The Laplaces S Equation Mathematics Stack Exchange




Partial Derivative If U X 2 Tan 1 Y X Y 2 Tan 1 X Y Prove ә 2u әxәy X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 Youtube
Show that the function y=c_1 e^x cos(x) c_2 e^x sin(x) satisfies the differential equation y''2y'2y=0 for any values of c1 and c2, then find the values for those constants that solve the initial value problem y(0)= 1, y'(0)= 1 math A polynomial that has zeros at 1, 2, and 3 with multiplicities of 1, 2, and 3 respectivelyGiven, u =tan−1( xyx2 y2 ) ⇒ tanu = (xy)x2 y2 On differentiating both the sides wrt x and y respectively, we get sec2udxdu = (xy)22x(xy)−(x2 y2)If u= tan^1(y^2/x) , show that x^2 d^2u/dx^2 y^2d^2u/dy^2 2xy d^2u/dxy^2 =sin2usin^2u



2




If Y Tan 1 X 2 Prove That 1 X2 2y2 2x 1 X2 Y1 2 Explain In Great Detail Mathematics Topperlearning Com Z68xug
Problem show that the function Z=tan^1(2xy)/(x^2y^2) satisfies the laplace equation I understand I need to take the partial with respect to X and the partial Find an equation of the tangent line to the curve (x^2)(e^y)(ye^x)=4 at the point (2,0) asked in CALCULUS by payton Apprentice implicitdifferntiation Problems on Partial Differentiation U=log(x^2y^2z^2) , U=tan^1(2xy/x^2y^2), Z=f(xay) Q(xay)M1 topic Linear Differential Equation with Variable coe
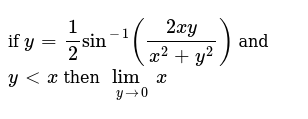



If Y 1 2sin 1 2xy X 2 Y 2 And Y X Then Lim Y 0 X



2




Section 2 6 Implicit Differentiation Section 2 6 Implicit Differentiation And Related Rates 28 Studocu



Partial Differential Equation Notes




If U Tan 1 X 2 Y 2 X Y Then Prove That X Brainly In



2



2




Show That Z Ln X 2 Y 2 2 Tan 1 Y X Satisfies The Laplaces S Equation Mathematics Stack Exchange



3 8 Implicit Differentiation Calculus Volume 1




Begin Array C Text If U Tan 1 Frac X 3 Y 3 Scholr




Ex 5 7 17 If Y Tan 1 X 2 Show X2 1 Y2 2x X2 1




If X2 Y2 2 Xy Find Dy Dx Mention Each And Every Step Mathematics Topperlearning Com Gwvwfskk



Problems On Partial Differentiation U Log X 2 Y 2 Z 2 U Tan 1 2xy X 2 Y 2 Z F X Ay Q X Ay Youtube



2




Solved Use The Chain Rule To Find The Indicated Partial Chegg Com



2




If Y Tan 1x 2 Show That X 2 1 2y2 2x X 2 1 2




Number 5 Please 1 14 Odes Integrating Factors Test For Exactness If Exact Solve If Not Use Homeworklib
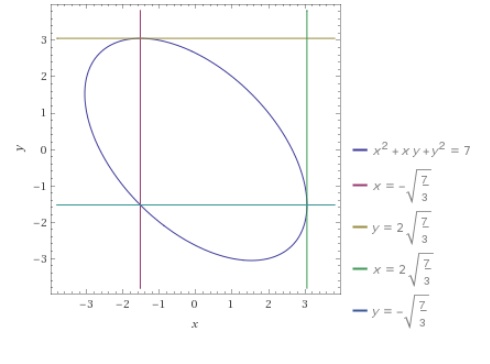



How Do You Find All Points On The Curve X 2 Xy Y 2 7 Where The Tangent Line Is Parallel To The X Axis And The Point Where The Tangent Line




Solved 1 If X R Cos 0 Y R Sin O Find A X Y Are Chegg Com



2
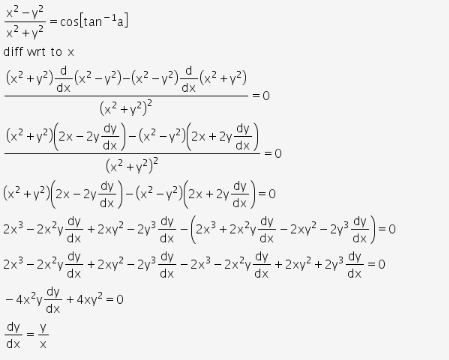



If Cos 1 X2 Y2 X2 Y2 Tan 1 A Prove That Dy Dx Y X Cbse Class 12 Learn Cbse Forum



2




A8ghahhhqyc3bm




Ex 5 7 17 If Y Tan 1 X 2 Show X2 1 Y2 2x X2 1
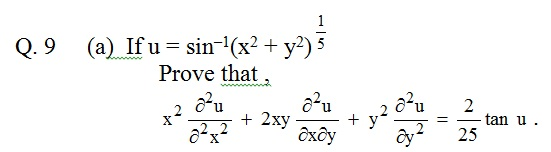



Solved If U Sin 1 X2 Y2 1 5 Prove That X2 2u 2x2 Chegg Com




Solved A X Y 1 If X R Cos 0 Y R Sin E Find A R 0 Chegg Com



2




If Tan 1 X2 Y2 X2 Y2 A Prove That Dy Dx X 1 Tana Y 1 Tana Brainly In




Linear Algebra Sheet 5 Summer 19 Warning Popup Annotation Has A Missing Or Invalid Parent Studocu
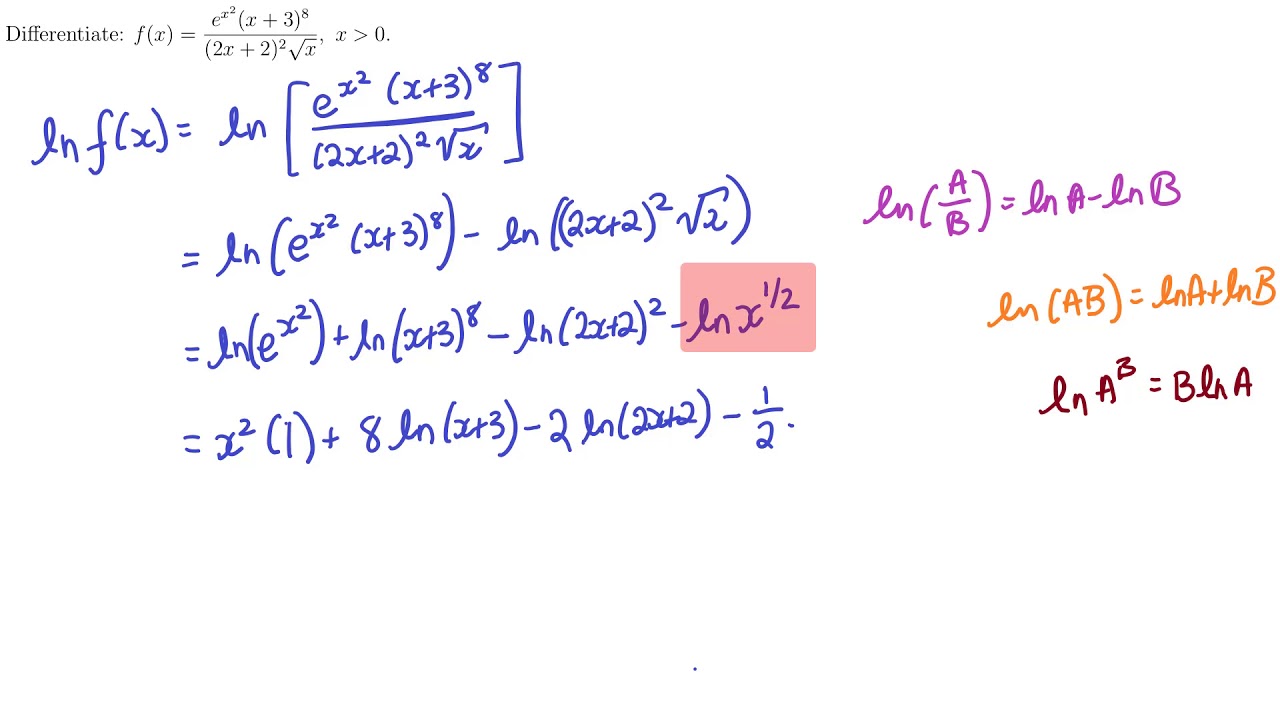



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation




Se13e01 01 Gif




Solutions To Implicit Differentiation Problems



If U Tan 1 X 2 Y 2 X Y Prove That X U X Y U Y 1 2 Sin 2u Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Ex 9 6 14 Find Particular Solution 1 X2 Dy Dx 2xy



3 1 63 46 8080




Eulers Partial Derivative Solve U Tan 1 X 3 Y 3 X Y Youtube
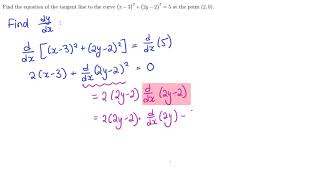



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation



If U Sin 1 X Y Then Prove That X U X Y U Y 1 2 Tan U Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



2



If U X 2tan 1 Y X Y 2tan 1 X Y Prove That 2u Y X X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



If U Tan 1 Y X Then Find D 2u Dx 2 D 2u Dy 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Problems On Partial Differentiation U Log X 2 Y 2 Z 2 U Tan 1 2xy X 2 Y 2 Z F X Ay Q X Ay Youtube



Partial Derivative Formula




If U Tan 1 X 2 Y 2 X Y Prove That X Delu Delx Y Delu Dely 1 2 Sin2u Youtube
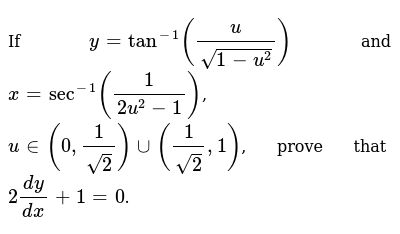



If Y Tan 1 U Sqrt 1 U 2 And X Sec 1 1 2u 2 1 U In 0 1 Sqrt2 Uu 1 Sqrt2 1 Prove That 2dy Dx 1 0




Solved X Y X Y 1 U Tan A If Aาน A U น 2xy Ox Chegg Com



Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy




Partial Derivatives Calculus 3
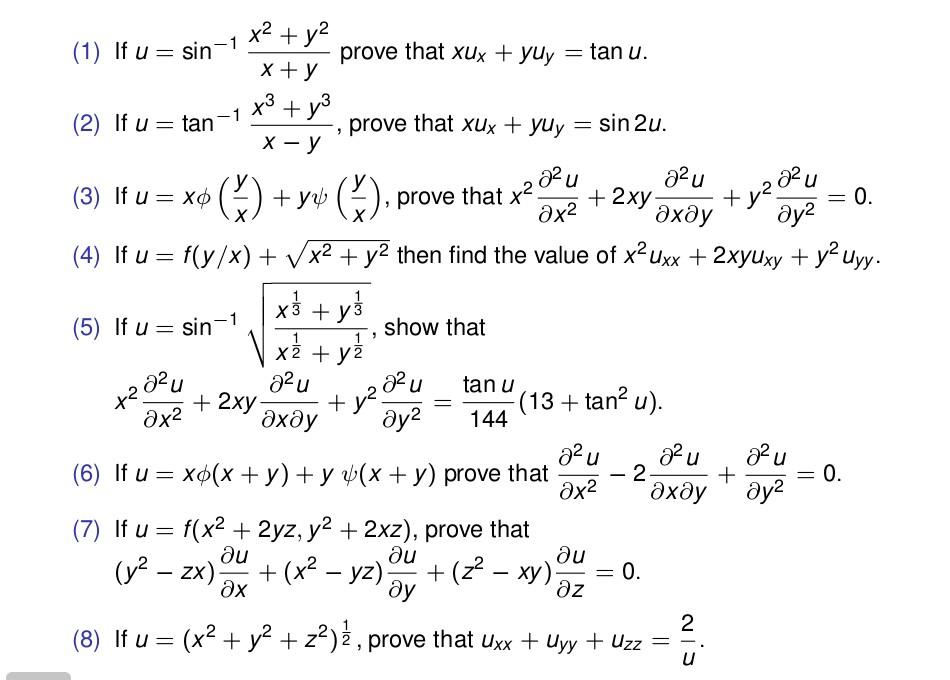



Solved A X Y 1 If X R Cos 0 Y R Sin E Find A R 0 Chegg Com




If Log X 2 Y 2 Tan 1 Yx Then Prove That Dydx X Yx Y




Ex 9 6 14 Find Particular Solution 1 X2 Dy Dx 2xy
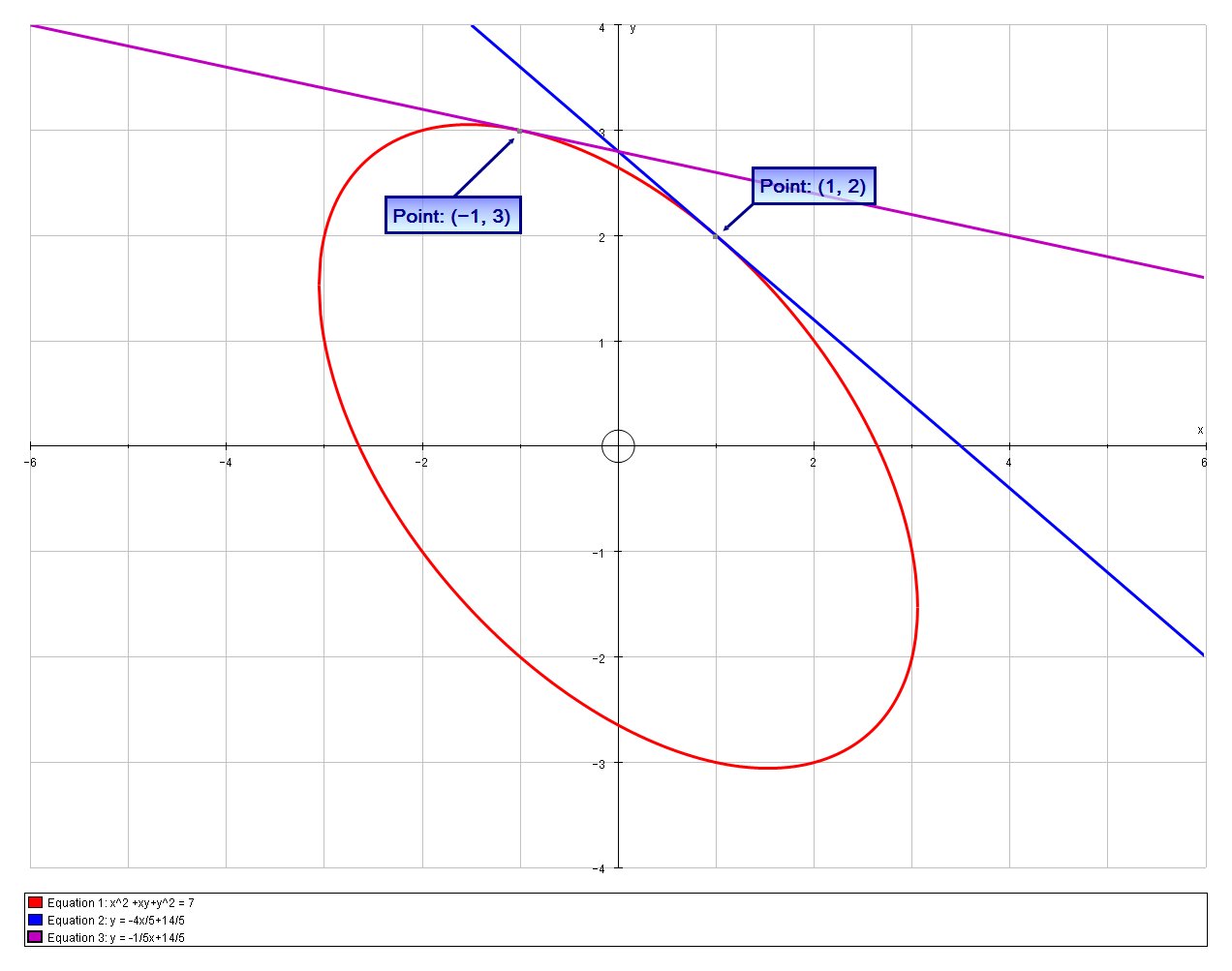



How Do You Find The Slope Of The Line Tangent To X 2 Xy Y 2 7 At 1 2 And 1 3 Socratic




Ex 9 2 9 Verify X Y Tan 1 Y Y2y Y2 1 0 Ex 9 2



If U Tan 1 X 3 Y 3 X Y Prove That X U X Y U Y Sin 2u Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



If U Tan 1 X 2 Y 2 X Y Prove That X U X Y U Y 1 2 Sin 2u Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



2




If Log X2 Y2 2tan 1 Y X Then Show That Dy Dx X Y X Y Brainly In




Misc 7 Show That General Solution Is X Y 1 A 1 X Y 2xy




If U Tan 1 X 2 Y 2 X Y Then X D U D X Yd U D Y



How Do L Solve The Initial Value Problem X 2 Y 2 Dy Dx Xy Y 1 2 Quora



3 8 Implicit Differentiation Calculus Volume 1




Answered 7 Y 9 Xy Y Vx 11 Xy 2y X X 0 Bartleby



2



Find Dy Dx When X And Y Are Connected By The Relation Tan 1 X2 Y2 A Studyrankersonline




How Do You Implicitly Differentiate 4 2x Y 2 Y 2x 3x 2y Socratic




Eulers Partial Derivative Solve U Tan 1 X 3 Y 3 X Y Youtube



2



How To Solve X 2 2xy Y 2 Dx Y 2 2xy X 2 Dy 0 Quora




If Y Tan 1 X Then 1 X 2 Y 2 2xy 1 A Y B 0 C 1 D 2




If U Log X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Verify 2u X Y 2u X Y



2



2



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation




Example 13 Solve Tan 1 2x Tan 1 3x Pi 4 Class 12



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿